Microbiology
Technical Services
Microbiologie | Services Techniques
Evaluating the performance of textile and polymeric materials against microbiological agents helps determine their potential applications in sports gear, medical fields, and protection and defense sectors. Agents such as bacteria, molds, fungi, and bacteriophages are used in various testing methods. This laboratory also assesses the biodegradability of textile and polymeric materials.

Biosafety Level 2
As a controlled Laboratory – Biosafety Level 2 (Public Health Agency of Canada), the CTT Group conducts performance evaluation and behavior testing of textiles, textile finishes, polymers, and geosynthetics when exposed to bacteria, fungi, molds, and bacteriophages.
These needs span multiple application sectors:
ANTIBACTERIAL PROPERTIES
Antibacterial treatments on textiles fall into two categories:
- Bactericidal treatments: lethal to bacteria on the textile
- Bacteriostatic treatments: inhibit bacterial growth
Several tests assess antibacterial effectiveness, each with a specific purpose:
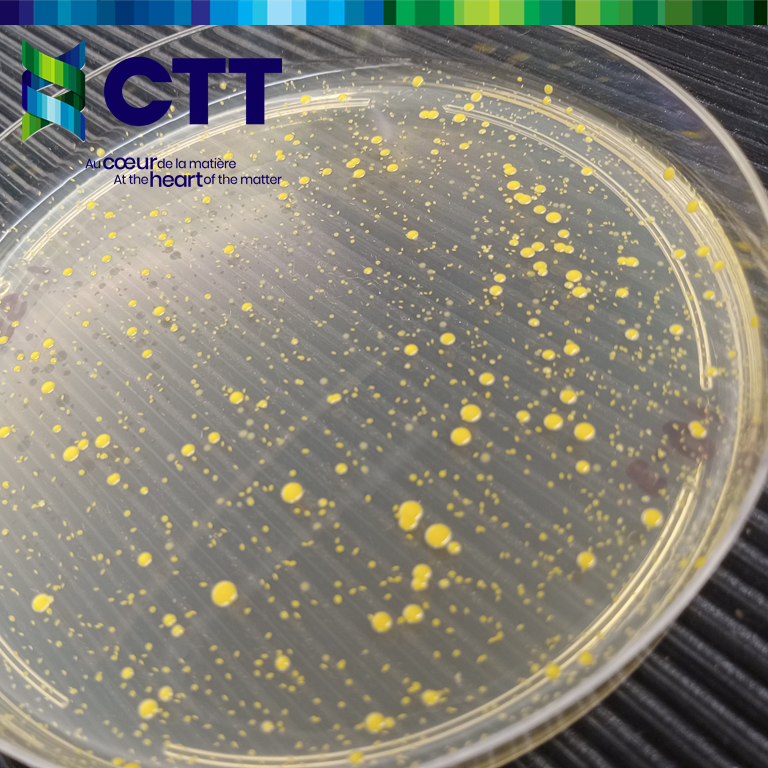
- Bioburden (microbial contamination level) is evaluated using ISO 11737-1. Microorganisms are assessed visually, requiring microbiological expertise.
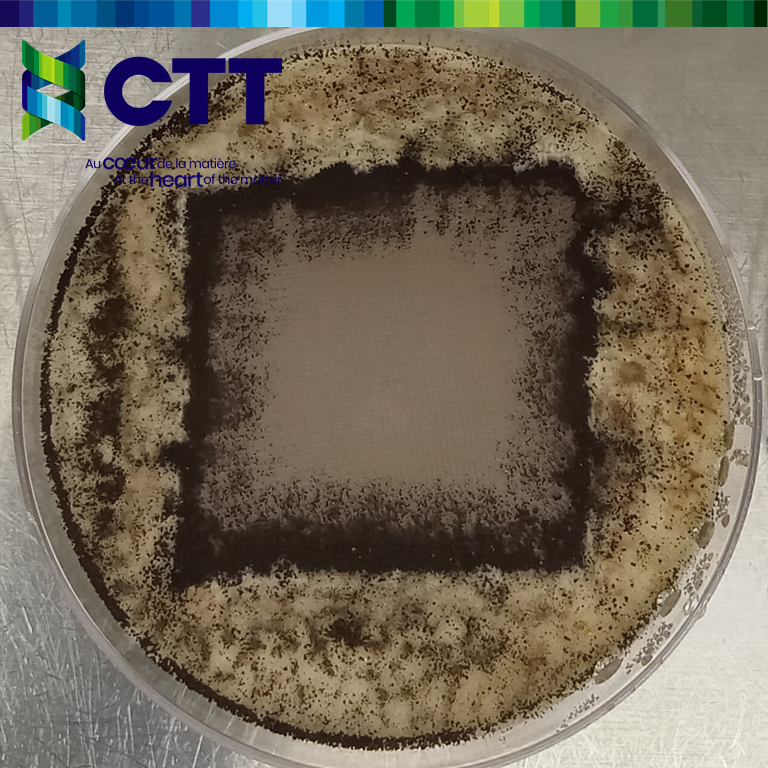
- AATCC 147 is used to visually observe bacteriostatic activity. A bacterial culture is streaked on agar, and the textile sample is placed on top. After 24 hours of incubation, the sample is examined for inhibition zones.
- Bactericidal activity is evaluated using AATCC 100 or ISO 20743. A known bacterial concentration is applied to the textile, incubated for 24 hours, and bacterial colonies are counted to determine the reduction percentage. Sampling can be done at various time intervals (e.g., 5 minutes, 1 hour, 24 hours).
- AATCC 211 is specifically designed to evaluate odor control performance in textiles treated with antibacterial agents.
Standard bacteria used in these tests include Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus vulgaris, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus. Custom strains can be used upon request.
ANTIFUNGAL PROPERTIES
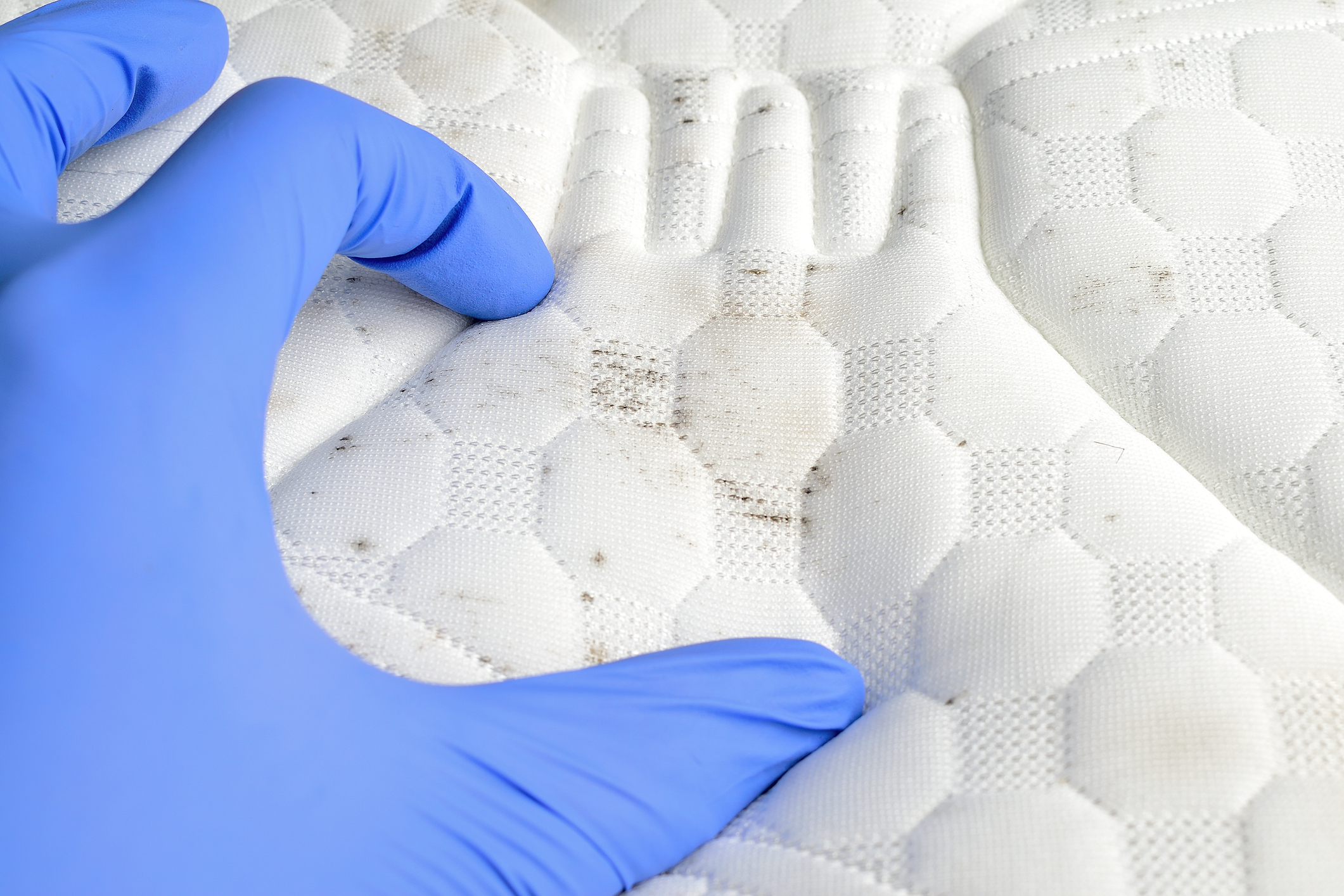
Antifungal treatments improve material durability when exposed to fungal spores (molds and fungi).
CAN/CGSB 4.2 No 28.2 and AATCC 30 Option III assess antifungal effects using Aspergillus niger. Samples are placed on a growth medium, inoculated with spores, and incubated. Fungal growth is evaluated on and around the sample.
Other methods under development include:
- CAN/CGSB 4.2 No 28.4 – evaluates fungal damage to textiles
- ASTM G21 – assesses fungal resistance of synthetic polymeric materials (mainly for building envelopes)
- ASTM G160 – evaluates microbial susceptibility of non-metallic materials buried in soil
VIRAL PENETRATION
For barrier textiles used in PPE, viral penetration resistance is a key test.
– ASTM F1671 evaluates resistance to blood-borne pathogens using the Phi-X174 bacteriophage. This test assesses barrier performance after exposure to the virus.
The following specifications use this test method :
BIODEGRADABILITY AND COMPOSTABILITY
As part of sustainable development research, the biodegradability of textile and polymeric materials is assessed using several methods. Samples are exposed to municipal waste inoculum under controlled temperature and humidity for a minimum of 15 or 45 days and until they reach the degradation threshold. Biodegradability is measured by the percentage of carbon converted to CO₂.
ASTM D5338
aerobic biodegradation under composting conditions with thermophilic temperatures
ASTM D5511
anaerobic biodegradation under high-solids digestion conditions (in development)
EXPERTISE AND DEVELOPMENT
CTT’s expertise in the behavior of textile and polymeric materials against microorganisms allows for investigative analyses, such as identifying the source of odors or stains, or rather, determine whether some samples are contaminated by fungi.
In product development projects, CTT creates antibacterial or antifungal formulations tailored to client needs. These antimicrobial formulations are designed for specific applications and adapted to their markets.
Here is some applications:
For more on antimicrobial mechanisms, refer to the book chapter written by our experts and collaborators:
Ibrahim, Ahmad, Laquerre, Joseph-Émile, Forcier, Patricia, Deregnaucourt Vincent, Decaens, Justine, Vermeersch, Olivier. ‘Antimicrobial Agents for Textiles: Types, Mechanisms and Analysis Standards’. Textiles for Functional Applications, IntechOpen, 22 Dec. 2021. Crossref, doi:10.5772/intechopen.98397.
External Links
AAMI : https://www.aami.org/
AATCC : AATCC Home – Recherche textile, méthodes de test et éducation depuis 1921.
ASTM : ASTM International | ASTM
CBRN : Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear and Explosive (CBRNE) Events – Canada.ca
Chapitre de livre : ‘Antimicrobial Agents for Textiles: Types, Mechanisms and Analysis Standards’
CSA : https://www.csagroup.org/
ISO : https://www.iso.org/
NFPA : https://www.nfpa.org